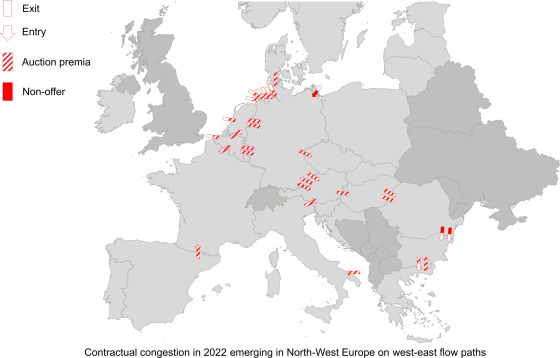
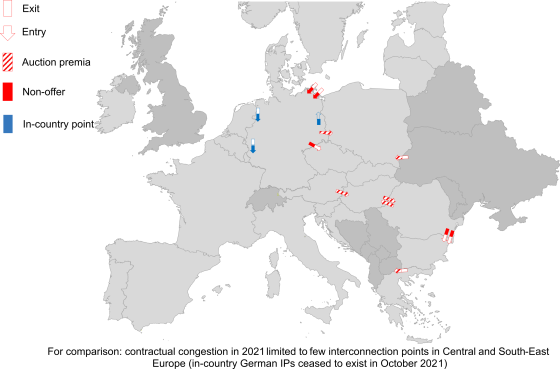
ENTSOG’s Summer Supply Outlook 2023 finds refilling of EU gas storages is on track

ENTSOG’s Summer Supply Outlook 2023 finds refilling of EU gas storages is on track
What is it about?
ACER publishes its Opinion on the 2023 Summer Supply Outlook of the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Gas (ENTSOG). ACER welcomes ENTSOG’s Outlook but recommends some targeted improvements to it.
ENTSOG’s Summer Outlook 2023 assesses the resilience of the European gas network for the summer of 2023 by examining the potential evolution of gas demand and supply. In particular, it analyses the likelihood of gas storage sites being filled to 90% of their capacity by 30 September 2023 (in line with Europe’s minimum gas storage filling obligations), considering the existing gas supply risks and the current dependence of the EU on Russian gas. With EU gas storage above 75% in early July 2023, Europe is on track to meeting the 90% target if current gas storage injection levels continue.
Highlights of ENTSOG’s Summer Supply Outlook
ENTSOG’s Summer Supply Outlook 2023 presents two scenarios:
- Minimised Russian gas imports; and
- Complete disruption of Russian pipeline supply.
Its main findings include:
- Reaching 90% storage filling levels by end of this summer is possible in both scenarios, if there is cooperation among EU countries.
- The existing gas infrastructure, including recently commissioned projects, can effectively reduce the dependency on Russian gas supply.
- In a 'cold winter' with full Russian pipeline disruptions (which is the harshest scenario), additional gas supplies and demand reduction would be required.
- Additional measures to improve the security of gas supply include:
- Increased liquified natural gas (LNG) imports (beyond historically observed import levels);
- Enhanced capacities provided by transmission system operators (TSOs), leading to shift in gas flow (from West to East); and
- Implementation of the existing target to reduce gas demand by 15%.
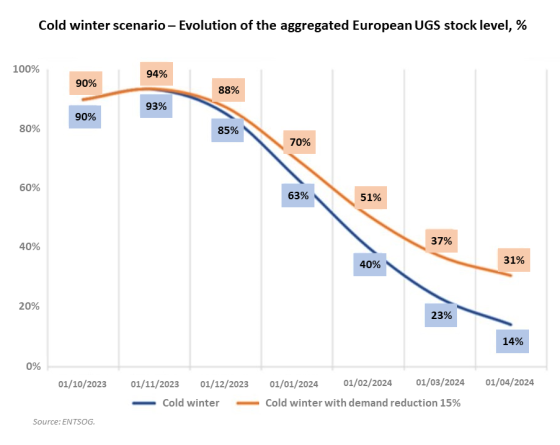
What is in the ACER Opinion?
- ACER appreciates that ENTSOG’s Outlook reflects already reduced gas flows from Russia and has a scenario of complete disruption of Russian gas.
- ACER welcomes that the recently commissioned infrastructure has added significant cross-border capacities and more than 30 bcm of LNG import capacities, improving the resilience of the EU gas system to import gas from sources other than Russia.
- ACER agrees with ENTSOG that additional LNG imports, enhanced transmission capacities and the implementation of a 15% gas demand reduction target may be needed to secure adequate levels of gas storage at the margins of 2023/24 winter season.
- ACER also stresses that continued vigilance regarding gas supplies and monitoring of storage filling trajectories are crucial because of the persistent risks of a significant reduction in Russian gas supply.
ACER’s main recommendations to ENTSOG for improving Outlook’s methodology and results:
- Use a complementary scenario based on expected gas supply and booked capacities;
- Estimate the effects of high gas prices on gas demand;
- Where relevant, adapt gas supply assumptions to potential events impacting the gas supply import capabilities, going beyond assumptions based on historic values;
- Use gas demand projections which are fully consistent with the European targets on gas demand reduction and phase-out of Russian gas; and
- Increase the level of granularity of the simulation results, the network topology, and its visualisation.
ACER highlights the importance of a close cooperation between ENTSOG and the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E) to ensure consistent assumptions and results in their respective seasonal outlooks.
Access the ACER’s Opinion on ENTSOG’s Gas Summer Supply Outlook 2023.
Also see the recent ACER communication on ENTSO-E’s Summer Outlook 2023.